





These sensors use laser or LED light to quickly and precisely measure distances on a wide range of materials, even at large ranges.




The I4.0-Capable sensor solution of the future.
As leading innovator in optical sensors, Leuze electronic positions itself as the driving force and pioneer for the implementation of Industry 4.0
Making sensor data and information from different sources availa- ble globally and linking this data and information in a meaningful way – this is the crux of Industry 4.0. New business ideas make it necessary to make this information globally available and accessi- ble not only within a company but also beyond the boundaries of the company and its location.
Products
OI – LINK
Compartment occupation sensors
Material thickness sensors
Sag/loop control
Parts detection and type testing
Detection of transparent objects
Measurement of roll diameter
Detection of contrast markers
Detection of objects in film
1D and 2D Codes
1D code
2D matrix code
2D stacked code
Radio Frequency Identification – RFID
Measuring Sensors
Optical distance sensors
Ultrasonic distance sensors
Sensors for positioning
3D sensors
Light curtains
Bar code positioning systems
Measuring forked sensors

OI-LINK
IO-Link: The standard for networked factories.
As founding member and technology developer of IO-Link, we have broad know-how and offer an extensive line of IO-Link sensors and system components such as IO-Link master and connection technology.
You always receive the latest technology – such as Smart Sensor Profile – and many sensors with additional functions as well as connection options to the cloud. With our networked solutions, you are ideally prepared for current and future requirements of the smart factory.
APPLICATION EXAMPLES
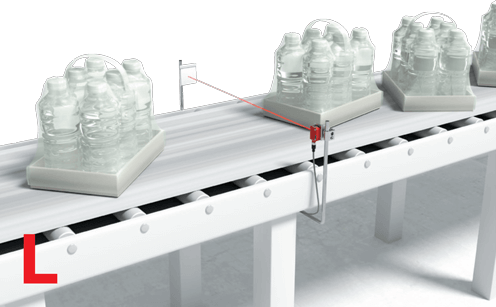
Compartment occupation check and push-through protection
Solution:
The diffuse sensors of the HT 10, 110 and HRT 25B series also detect a wide range of pallets and containers. With their precise switching points, they can be used on nearly every high-bay storage device for compartment occupation checks or for push-through protection.
Material thickness measurement

Solution:
The ODSL 8 and ODS 9 sensors measure the distance with resolutions of up to 0.01 mm and thereby supply the basis for a high quality of this process step.
Sag/loop control

Solution:
The tension of the material can be monitored by measuring the sag. Due to their various light-spot geometries, the ODSL 8, ODS 10 and ODSL 96 sensors can reliably measure the sag of a wide range of different material surfaces.
APPLICATION EXAMPLES
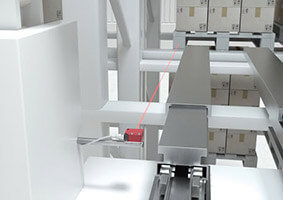
Parts detection and type testing
Solution:
Our compact and switching TOF sensors ODS 110 / HT 110 are the perfect solution – even in situations with limited installation space. Models ODS / HT 10 are suitable for measurement ranges over 5 m. They can also be mounted outside of the robot cells.
Detection of transparent objects

Solution:
Through the use of a retro-reflective photoelectric sensor for transparent objects with IO-Link – such as our PRK 3C, PRK 55 or PRK 18B – environmental influences can be detected and analyzed so that the machine control can respond.
Measurement of roll diameter

Solution:
An optical or ultrasonic distance sensor – such as ODS 9 or ODS 96B – measures the distance from the sensor to the roll. The measurement values are digitally transmitted to the machine control via the IO-Link process data. No conversion of measurement values from analog to digital is necessary.
APPLICATION EXAMPLES
Detection of contrast markers

Solution:
An optical contrast sensor – such as the KRT 3B or KRT 18B – is used that determines the optimum contrast ratios by means of multiple transmitter colors. The transmitter colors are taught in once using a teach routine and stored in the sensor or control. IO-Link can then be used to select defined and taught products from the recipe memory of the sensor or transfer them from the control. No new teach-in process is necessary.
Detection of objects in film

Solution:
The measuring light curtain of type CML 730 with power setting transilluminates the only partially transparent films with its transmitter that has been set to high power. The number and position of the interrupted beams is output to the machine control via the IO-Link interface. Preset, material-dependent beam parameters can be output to the light curtain via IO-Link.

1D AND 2D CODES
The Right Technology.
To offer the optimum solution for all requirements, we use various technologies. These range from optically reading 1D and 2D codes to contact-free data transmission through radio frequency identification.
1D CODE
With 1D codes, the information is represented using lines and gaps of various widths. The black bars and white gaps reflect the light emitted by the 1D code reader to different degrees. Less light is reflected by the black bars. This is detected by the receiver module of the reader, which converts the information into binary data that can subsequently be processed further and output via an interface.
ADVANTAGES
Simple and inexpensive to create.
Through an integrated check digit, the code is directly checked for validity, thereby making possible high first-pass read rates.
AREAS OF APPLICATION
Electronics, automotive and consumer goods industries.
Transport logistics.
Postal shipping.

2D CODE
There are two types of 2D codes: the matrix code and the stacked code.
With the matrix code, the information is represented by arranging small geometric cells.
The stacked code is a special case. Here, the information is represented by lines and gaps in multiple rows. The camera of the sensor takes a picture of the code. The camera chip detects the contrast between the white gaps and the black cells and converts the information into binary data. This is then processed further and output via an interface.
Unlike the 1D code, the information is contained in the arrangement of the cells.
2D matrix code
ADVANTAGES
Minimal space requirement.
Highest-possible information content.
Through the integrated error correction algorithm, even damaged codes can be read error-free.
AREAS OF APPLICATION
Transport logistics.
Electronics and automotive industries.
Consumer goods and travel sectors.
Pharmaceutical industry.

2d stacked code
ADVANTAGES
Compact code compared to 1D codes.
Variable width and height.
Through the integrated error correction algorithm, even damaged codes can be read error-free.
AREAS OF APPLICATION
Transport logistics.
Consumer goods industry.
Travel sector.


RADIO FREQUENCY IDENTIFICATION – RFID
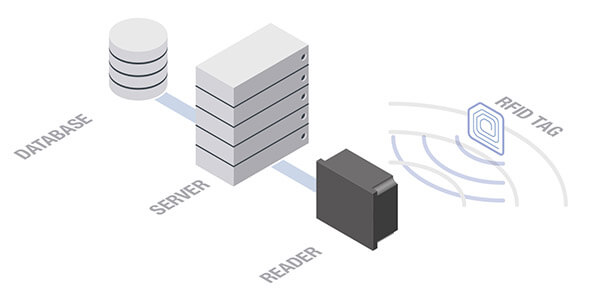
Radio Frequency Identification – RFID.
An RFID system consists of a read/write system with integrated and/or external antenna as well as at least one transponder and uses electromagnetic waves for data transmission. Each transponder consists of an antenna and a microchip on which a unique, unchangeable serial number (Unique ID) as well as – depending on the type of transponder – other object-related data is stored.
While active transponders use an integrated power source for data transmission, passive transponders draw the energy required for data transmission from the electromagnetic field of the reader. Here, RFID systems use either low frequencies/LF (125 kHz to 134 kHz), high frequencies/HF (13.56 MHz) or ultra-high frequencies/UHF (865 MHz to 928 MHz). The used frequencies vary depending on operating range, transmission rate and susceptibility to interference. In general, the reading ranges achieved by the system increase with frequency, but so too does the susceptibility to interference.
ADVANTAGES
“Visual contact” is not required between write/read unit and transponder: the radio waves penetrate materials such as wood, cardboard or plastic depending on the frequency range.
Transponders can be integrated in the product or in the transport medium.
RFID systems are robust and also function reliably in harsh environments independent of contamination.
When using writable transponders, production and quality data can be stored directly on the transponders during the production process.
AREAS OF APPLICATION
Production control.
Access control.
Identification of persons and objects.
Skid, container and pallet identification.
Material flow control in conveyor and storage systems or the automotive industry.

MEASURING SENSORS
Intelligent monitoring and control through measuring sensors.
Measuring sensors can actively check distances, position system parts and monitor other parameters in order to intelligently and independently initiate actions and, e.g., intervene in processes for control purposes. Here, you will find a large selection of technologies and designs for as efficient and fault-free system operation as possible.
Optical distance sensors

Lights on – measurement starts.
These sensors use laser or LED light to quickly and precisely measure distances on a wide range of materials, even at large ranges.
Ultrasonic distance sensors

When light isn’t enough.
With ultrasonic technology, it is possible to reliably detect even partially or completely transparent objects and to perform reliable distance measurements. In addition, measurements can be performed in dusty, hazy or humid environments.
Sensors for positioning

At the right position with millimeter accuracy.
With moving system parts that need to automatically work together, the positioning of parts or work pieces with millimeter accuracy is of great importance. We offer devices here with two operating principles. One is a laser distance measurement device that measures against a reflector and the other is a bar code positioning system that has a red light laser which determines the position and speed relative to a bar code tape.
3D sensors

Would you like another dimension with that?
These sensors determine height contours. 3D data can be easily generated for moving objects or by moving the sensor. The measurement data can either be output for external processing or preprocessed in the sensor for convenient object measurement or detection.
Light curtains

Many beams see more than one.
Our measuring light curtains monitor a large measurement field and output measurement information from this field. Depending on the configuration and model, the devices are suitable for a variety of measurement tasks with various resolutions and can be integrated in different fieldbus environments.
Bar code positioning systems

Position data without limit – “Infinite”, curve-going and with millimeter accuracy.
The read head of the bar code positioning system is moved along a bar code tape. It calculates the absolute position data in the direction of travel with millimeter accuracy up to a distance of 10,000 m. The bar code tape is extremely simple to use and can be bonded both in straight lines and in curves. Maximum flexibility, simple mounting, transparent diagnosis as well as a large selection of integrated interfaces are the strengths of this system.
Measuring forked sensors




Fork is just another word for exact.
The forked shape offers measurement resolutions as great as 0.014 mm with high reproducibility without time-consuming alignment. An infrared light-band illuminates a line-scan camera (CCD line) and returns analog or digital output signals depending on the illuminated pixels and configuration.